Overview
Teaching: 15 min Exercises: 15 minQuestions
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using tools like Make?
Objectives
Understand advantages of automated build tools such as Make.
Automated build tools such as Make can help us in a number of ways. They help us to automate repetitive commands and, so, save us time and reduce the risk of us making errors we might make if running these commands manually.
They can also save time by ensuring that automatically-generated artifacts (such as data files or plots) are only recreated when the files that were used to create these have changed in some way.
Through their notion of targets, dependencies and actions they serve as a form of documentation, recording dependencies between code, scripts, tools, configurations, raw data, derived data, plots and papers.
Creating PNGs
Add new rules, update existing rules, and add new macros to:
- Create
.pngfiles from.datfiles usingplotcount.py.- Add the
zip_test.pyscript as dependency of theresults.txtfile- Remove all auto-generated files (
.dat,.png,results.txt).Finally, many Makefiles define a default phony target called
allas first target, that will build what the Makefile has been written to build (e.g. in our case, the.pngfiles and theresults.txtfile). As others may assume your Makefile confirms to convention and supports analltarget, add analltarget to your Makefile (Hint: this rule has theresults.txtfile and the.pngfiles as dependencies, but no actions). With that in place, instead of runningmake results.txt, you should now runmake all, or just simplymake. By default,makeruns the first target it finds in the Makefile, in this case your newalltarget.Solution
This Makefile and this
config.mkcontain a solution to this challenge.
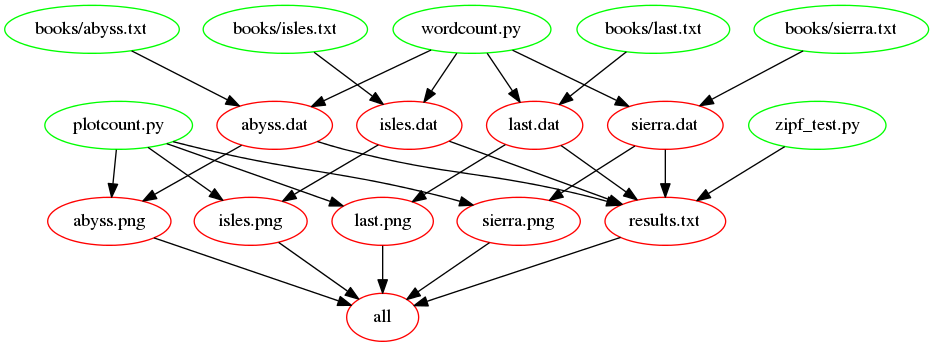
The following figure shows the dependencies involved in building the all target, once we’ve added support for images:
Creating an Archive
Add new rules, update existing rules, and add new macros to:
- Define the name of a directory,
zipf_analysis, to hold all our code, data, plots and the Zipf summary table.- Copy all our code, data, plots and the Zipf summary table to this directory.
- Create an archive,
zipf_analysis.tar.gz, of this directory. The bash commandtarcan be used, as follows:$ tar -czf zipf_analysis.tar.gz zipf_analysis
- Update
allto createzipf_analysis.tar.gz.- Remove
zipf_analysisandzipf_analysis.tar.gzwhenmake cleanis called.- Print the values of any additional variables you have defined when
make variablesis called. > ## Solution > This Makefile > and thisconfig.mk> contain a solution to this challenge.
Archiving the Makefile
Why do we add the Makefile to our archive of code, data, plots and Zipf summary table?
Solution
Our code (
wordcount.py,plotcount.py,zipf_test.py) implement the individual parts of our workflow. They allow us to create.datfiles from.txtfiles,.pngfiles from.datfiles andresults.txt. Our Makefile, however, documents dependencies between our code, raw data, derived data, and plots, as well as implementing our workflow as a whole.
Key Points
Makefiles save time by automating repetitive work, and save thinking by documenting how to reproduce results.